How to get started with RTK on ArduPilot (and dual antenna heading too)


Get started with Ardupilot
If you’re developing a project related to unmanned vehicles like drones (UAVs), rovers, boats, or even submarines, enabling autonomous navigation requires integrating autopilot with a precise GNSS/RTK location system. While the integration process can be challenging, we have prepared this article to help you to get started.
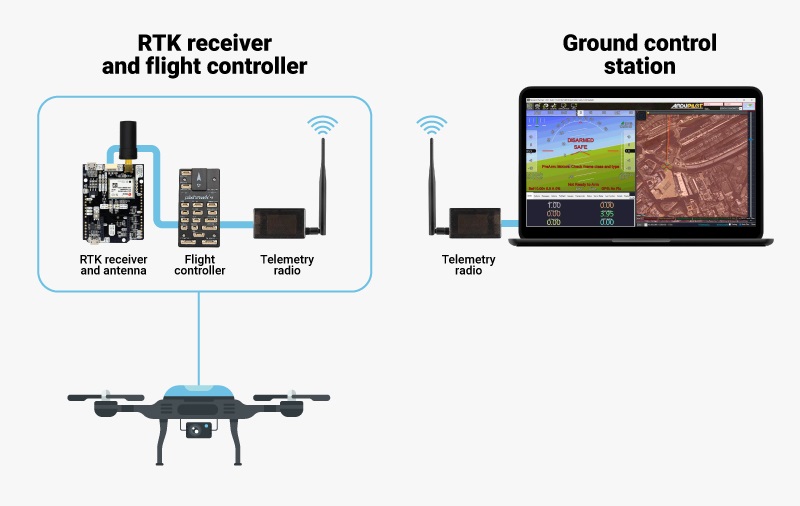
What are ArduPilot, Flight controller and Ground control station?
The Flight controller is the hardware component that runs the ArduPilot firmware, acting as the central “brain”. It processes input from various sensors (like GPS, accelerometers, and gyroscopes) to stabilize and control the vehicle. Popular flight controllers compatible with ArduPilot include the Pixhawk, Cube, and Navio2.
In most of out tutorial we tests with Pixhawk 4, you will need to adjust some parameters in other flight controllers.
Ground Control Station is software application, running on a computer, phone or transmitter, that communicates with your UAV via wireless telemetry or USB cable. Mission Planner and QGroundControl are two widely used ground control stations compatible with ArduPilot. You can use it to configure, control and monitor your unmanned vehicles.
How to choose a GNSS/RTK receiver for ArduPilot project?
Integrating a GNSS/RTK receiver into an ArduPilot project provides precise GNSS positioning and navigation for more accurate and reliable autonomous operations.
You need centimeter accurate GPS location only
If your ArduPilot project requires the drone to repeatedly follow the same flight path, hover, navigate, and land within a few centimeters of a set waypoint, a GPS/RTK receiver with a single antenna is sufficient as it provides precise GNSS positioning. In this case, we recommend these GNSS/RTK boards:
- simpleRTK2B Budget (powered by u-blox ZED-F9P) as the most affordable option.
Key features:
– Down to centimeter GPS accuracy
– Up to 10 RTK position updates per second
-
Sale!
 Made in EuropeRTK2B Boards
Made in EuropeRTK2B BoardssimpleRTK2B Budget
From 167,00€ This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
- simpleRTK3B Pro (powered by Septentrio Mosaic-X5) for anti-jamming and anti-spoofing capabilities.
Key features:
– Down to 10 millimeters GPS accuracy
– Up to 50 RTK position updates per second
– Anti-jamming and anti-spoofing capabilities
- simpleRTK3B Pro (powered by Septentrio Mosaic-X5) for anti-jamming and anti-spoofing capabilities.
-
RTK3B Boards
simpleRTK3B Pro
From 569,00€ This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
These boards are suitable for scenarios requiring precise positioning but not high heading accuracy, such as waypoint missions or terrain mapping.
You need GPS location + dual antenna heading
In this case we recommend simpleRTK3B Compass powered by Unicore UM982 receiver.
Key features:
- Down to 10 millimeters GPS accuracy
- Heading accuracy of 0.1° per meter of Baseline distance
- Up to 50 RTK position updates per second
- Basic jamming immunity
How to set up GNSS/RTK receiver with ArduPilot?
To guide you through the process of setting up your receiver and using it with ArduPilot, we have prepared several tutorials.
Connect and configure your GNSS/RTK receiver
- Follow our tutorials to configure your GNSS/RTK receiver:
Enable centimeter-level accuracy with RTK corrections
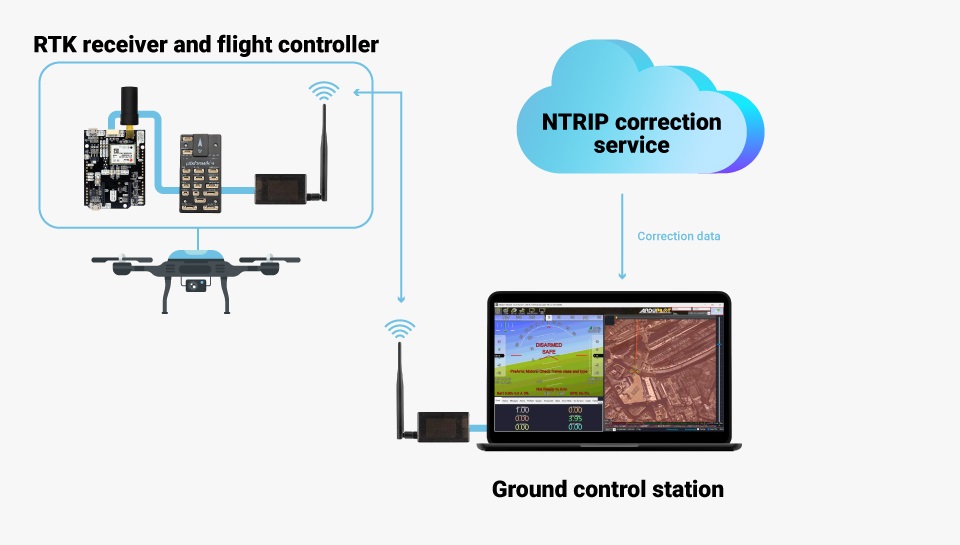
- To achieve centimeter-level precision in positioning, RTK correction data must be sent to your drone in real time. There are two main methods for delivering this correction data:
- Using NTRIP correction service: This method is convenient for areas with reliable internet connection and NTRIP service coverage. If you are not aware of NTRIP service provider in your area, we have prepared the List of RTK correction service providers in your country. If this is your case, follow our tutorial on sending NTRIP corrections to ArduPilot.
-
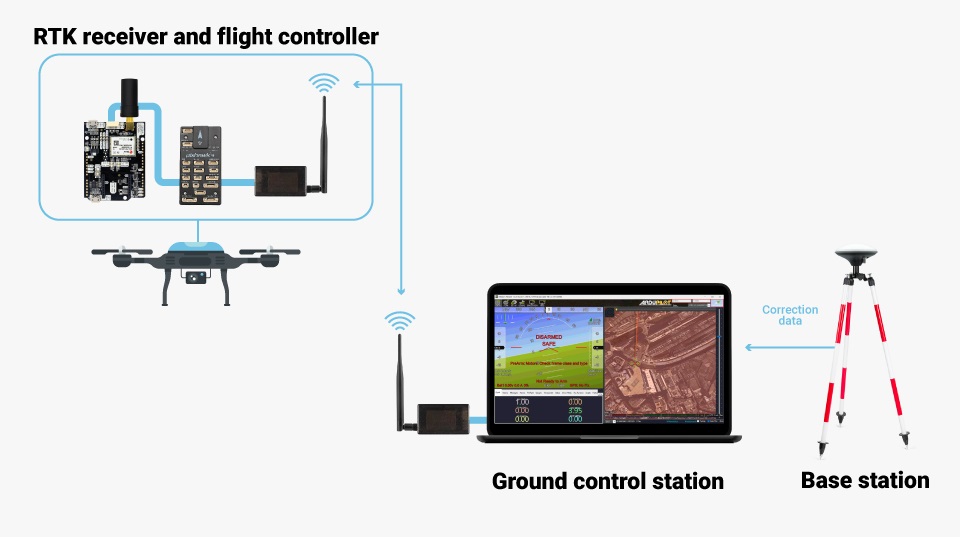
- Using RTK corrections from a Base Station: This method is useful in areas where there is no internet access or NTRIP correction service available, but it requires extra equipment: wireless link between your Base and drone (Rover) and a Base station itself. You can refer to ArduSimple’s tutorial on sending RTK corrections from Base station to ArduPilot for detailed instructions.
 and
and