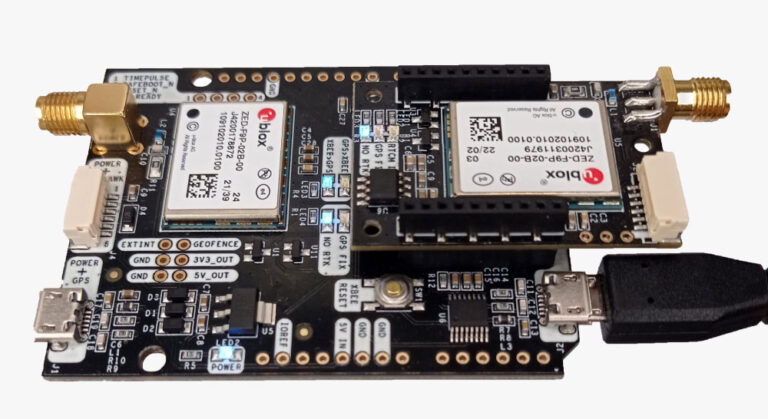
How to connect simpleRTK2B Heading to ArduPilot with external RTK corrections?

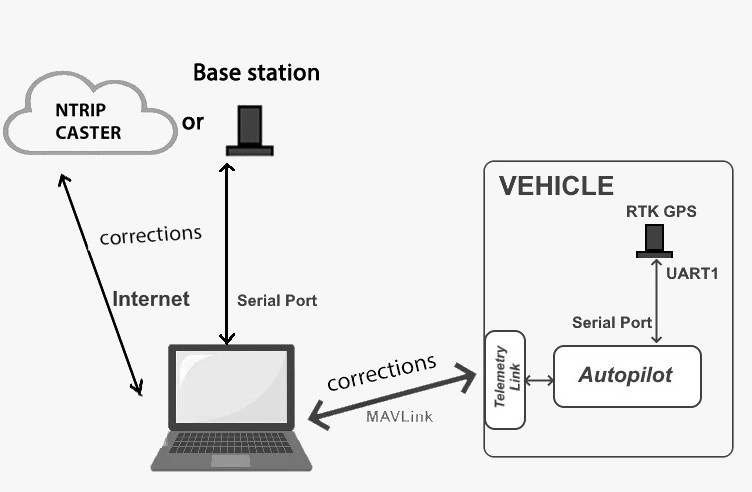
This tutorial is useful for you if you want to use the simpleRTK2B Heading kit with external RTK corrections sent via MissionPlanner or QGroundControl.
Required hardware:
- simpleRTK2B Heading – Basic Starter Kit
- USB to micro-USB cable
- Pixhawk cable set
- Holybro Pixhawk4 (you can use your preferred autopilot)
- a PC or laptop
Required software:
- Mission Planner
- u-center ( for M8, M9, F9)
Important things before start:
- This tutorial is based on the simpleRTK2B Heading – Basic Starter Kit, if you have a different hardware you may need to apply some changes in this tutorial.
We have prepared another tutorial for the simpleRTK3B Heading. - We have validated the tutorial with this autopilot:
- Holybro Pixhawk4
- We have validated the tutorial with this firmware version:
- ArduCopter 4.1.5
- ArduPilot programmers introduced restrictive conditions to let your autopilot use GNSS based heading, here a few of them:
- You need good RTK fix so it is mandatory to place both antennas in a good location (outdoors, no trees, no high buildings around).
If you try to follow this tutorial inside your house with the antennas close to your window, it will not work. - Place both antennas away from each other (distance between antennas should be >30cm and <5m).
If you place the antennas next to each other, it will not work.
Place the antennas in the X axis of your rover (forward direction). You can change this later. - Place both antennas in a plane parallel to your autopilot plane (i.e. if your autopilot is horizontal, place both antennas at the same height above ground).
If the antennas are not placed at the same height level with respect your plane/rover/copter you will need to set the parameter GPS_POS1_Z, otherwise it will not work
- You need good RTK fix so it is mandatory to place both antennas in a good location (outdoors, no trees, no high buildings around).
- Do not connect the GNSS receivers with the autopilot yet, we will configure everything independently and connect everything afterwards
How to configure your simpleRTK2B heading kit to connect to ArduPilot and receive external RTK corrections?
In the simpleRTK2B+heading Basic Starter Kit:
- simpleRTK2B (big board) acts as a base in the moving base configuration
- simpleRTK2Blite (small board) acts as a rover in the moving base configuration
- The configuration file works on firmware 1.13 of ZED-F9P.
Firstly, configure simpleRTK2B receiver (aka big board).
- Connect the simpleRTK2B to your PC via the USB port labeled POWER+GPS.
- Run u-center and connect your receiver via COM port.
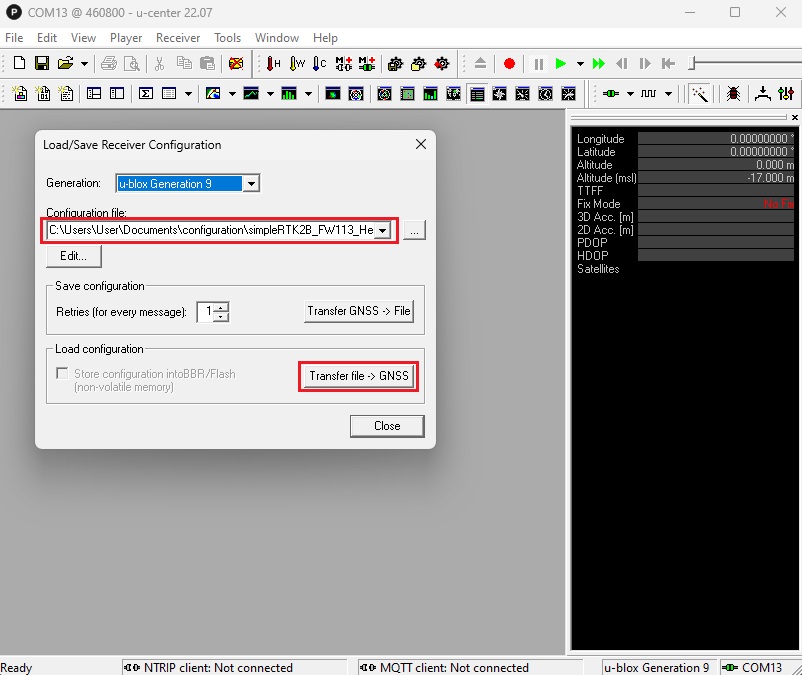
- Go to Tools –> Receiver Configuration …. Select configuration file simpleRTK2B_FW113_HeadingKit_extcorrections_simpleRTK2B_5Hz-00.txt.
Click Transfer file–>GNSS.
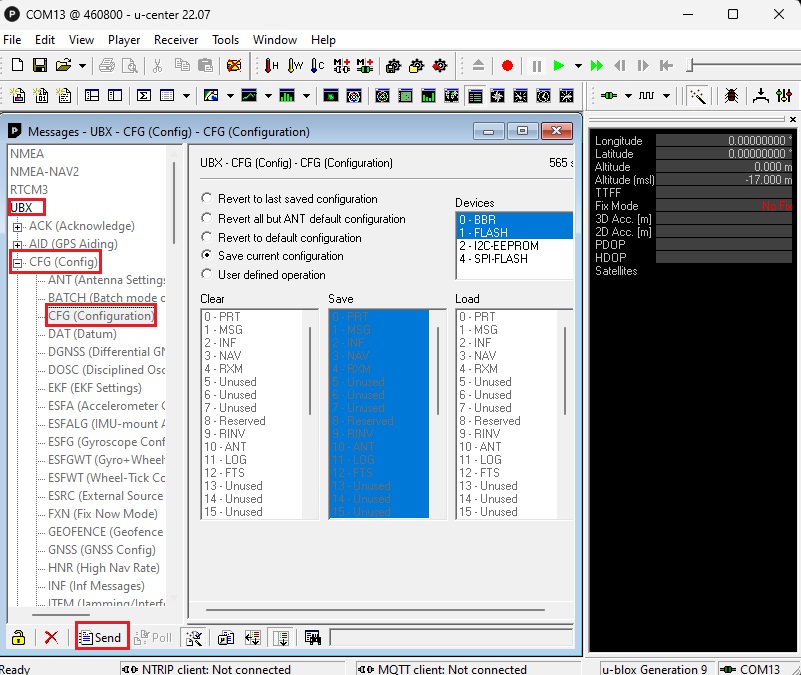
- Go to View–>Messages View–>UBX–>CFG–>CFG. Select Save current configuration and click Send.
Secondly, configure simpleRTK2B Lite receiver (aka small board).
- Make sure the simpleRTK2B Lite board is mounted on top of the simpleRTK2B board.
- Connect the board to your PC via the USB labeled as POWER+XBEE. This USB port will let you communicate with the simpleRTK2B Lite board via its UART1.
- Run u-center and connect your receiver via COM port.
- Go to Tools –> Receiver Configuration ….Select configuration file simpleRTK2B_FW113_HeadingKit_extcorrections_simpleRTK2Blite_5Hz-00.txt Click Transfer file –> GNSS
Note that depending on your previous configuration, you may need to upload the configuration file twice because there is a baudrate change in the middle of the configuration file.
- Go to View–>Messages View–>UBX–>CFG–>CFG. Select Save current configuration and click Send.
Thirdly, load ArduPilot configuration file.
- Connect your Pixhawk to your computer using a USB to micro-USB cable.
- Open Mission Planner and connect your Pixhawk to it with COM port.
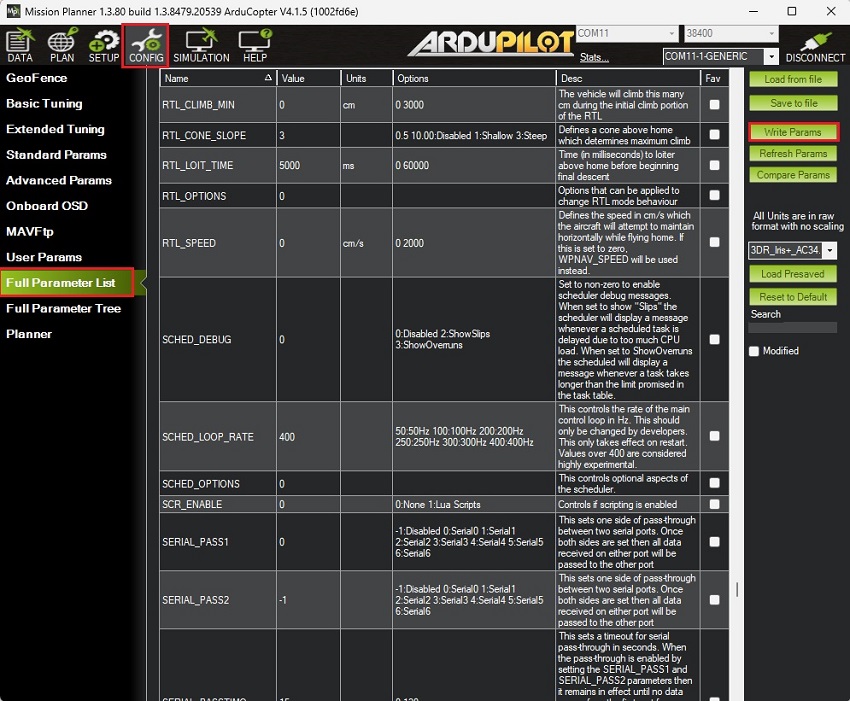
- Go to CONFIG–>Full Parameter List.
Given that the firmware versions might differ from yours, below is a list of all parameters that have been modified compared to the default configuration:COMPASS_ENABLE,0
COMPASS_USE,0
COMPASS_USE2,0
COMPASS_USE3,0
EK3_MAG_CAL,2
EK3_SRC1_YAW,2
GPS_AUTO_CONFIG,0
GPS_AUTO_SWITCH,0
GPS_POS1_X,-1.25 *This value must contain the distance in meters between antennas. Change sign if heading has a 180deg offset (or swap SMA connectors in simpleRTK2B+heading).
GPS_PRIMARY,1
GPS_RATE_MS, 200
GPS_RATE_MS2, 200
GPS_TYPE,17
GPS_TYPE2,18
SERIAL1_BAUD,460
SERIAL1_OPTIONS,0
SERIAL1_PROTOCOL,5
SERIAL2_BAUD,460
SERIAL2_OPTIONS,0
SERIAL2_PROTOCOL,5Press Write Params to save your setting.
- After saving all the parameters, make sure you remove the power from your autopilot by disconnecting USB cable to reset your autopilot.
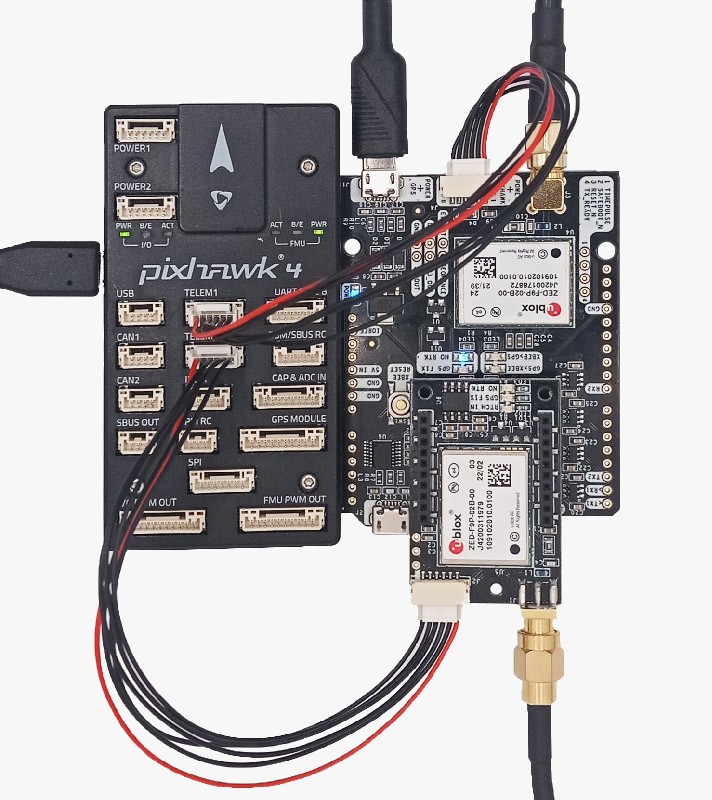
Finally, connect the heading kit to your autopilot.
- Make sure your already finish the initial set up of your autopilot. You can check the user guide of ArduPilot to see how to do it.
- Use the JST connector on the simpleRTK2B (big board) and connect it to the TELEM1 port.
Use the JST connector on the simpleRTK2B Lite (small board) and connect it to the TELEM2 port.
Connect your big board to PC with the USB port labeled with POWER+GPS. - Connect the antennas to your receiver. Make sure your antennas are completely in open air, meet the requirements of ArduPilot as we mentioned at the beginning.
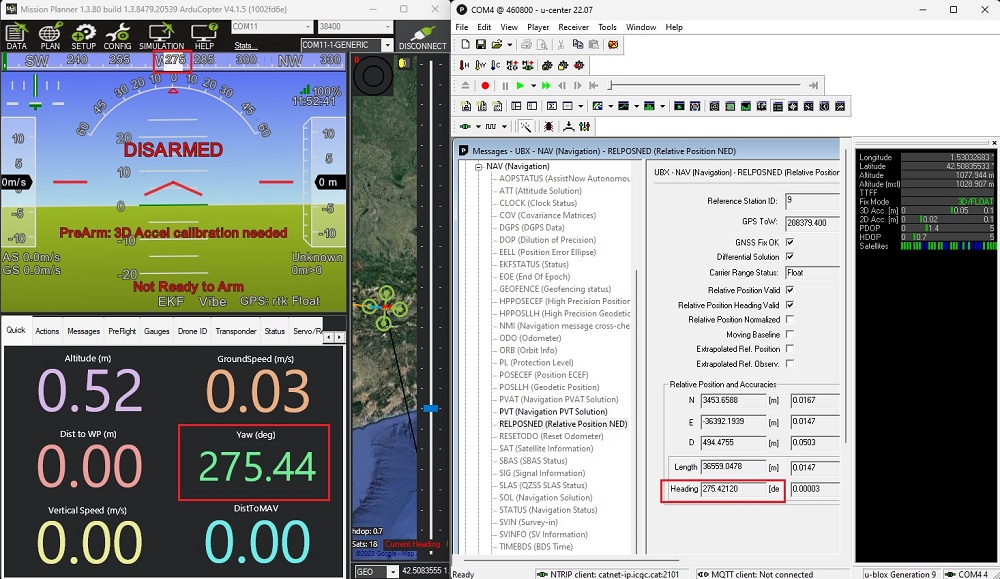
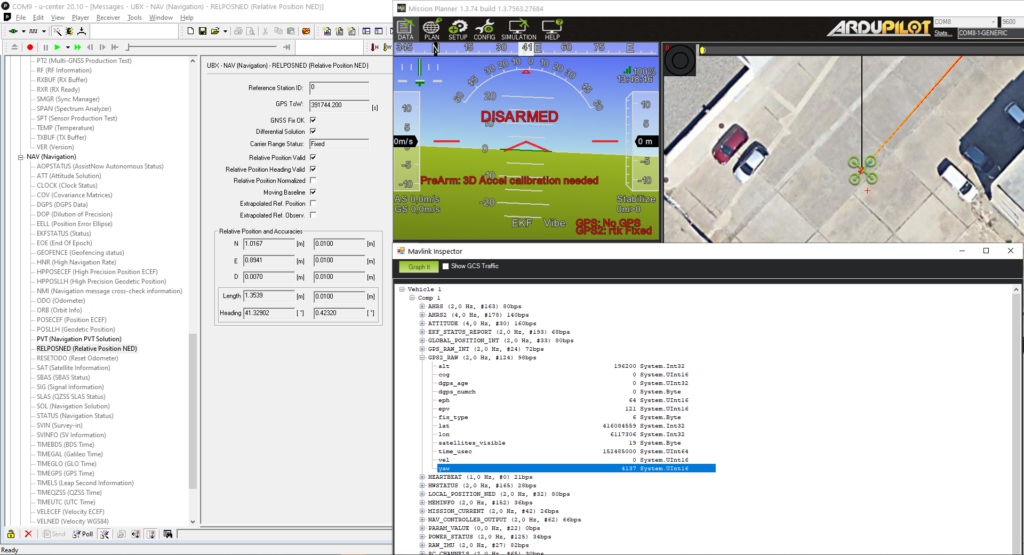
- Power the autopilot and wait a few seconds. Check the AHRS heading value on Mission Planner, it should match the direction between your antennas.
You can also check the Heading value of your antennas using u-center by following View–>Messages View–>UBX–>NAV–>RELPOSNED in the software.
- For an additional verification, ensure that the heading value in the AHRS matches the one found in CTRL+F–>MAVlink inspector–>GPS2_RAW–>yaw.
- Now you can send RTK corrections from your ground control station to your autopilot, these tutorials may help you:
Again, remember that the GNSS-based yaw might not function correctly if:
- Fix type is not RTK fix
- Antenna distance is not within 20% of the GPS1_POS_X parameter
- Autopilot attitude does not match antenna height difference
 and
and