How to determine the exact position of your base station with simpleRTK3B Pro

In the previous tutorial on configuring the simpleRTK3B as a static base station, we demonstrated the process of establishing the reference position using Septentrio’s auto mode.
While this method provides a fundamental reference with good pass-to-pass accuracy, achieving high absolute accuracy for the rover requires the utilization of an exceptionally precise reference position.
There are three ways of determining the geodetic reference position of your base station:
While this method provides a fundamental reference with good pass-to-pass accuracy, achieving high absolute accuracy for the rover requires the utilization of an exceptionally precise reference position.
There are three ways of determining the geodetic reference position of your base station:
- Using a known reference point Setting up the base station antenna above a known reference point, such as a geodetic control point or survey marker, offers a convenient method for acquiring a reliable reference position for the base receiver.
- Using NTRIP service You can connect to a NTRIP service to receive correction data. By logging the RTK positions and averaging them, it is possible to obtain a highly accurate reference position in a short amount of time.
- Using an online PPP post-processing service If there is no reference point or RTK network in your region, don’t worry, you can calculate the position of the base station by using an online Precise Point Positioning (PPP) service.
This approach is particularly suitable for users with an easy access to an accurate and up-to-date reference point.
This method proves beneficial for users situated in regions with access to an NTRIP service or RTK network.
Popular services include CSRS-PPP service, OPUS and APPS. Generally, these services recommend a minimal log file duration (usually 1-3 hours) and an ideal duration (typically 24 hours).
Some PPP services might require antenna calibration. If so, ensure you have a calibrated antenna like Calibrated Survey GNSS Tripleband + L-band antenna (IP67).
In this tutorial we will use CSRS-PPP service. You can receive a rapid result in about few hours. For the most accurate result, you might have to wait for 12-18 days.
Required hardware:
- simpleRTK3B Pro
- Budget Survey Tripleband GNSS Antenna
- USB to USB-C cable
- a PC or laptop with internet access
Required software:
- STRSVR of RTKLIB (Optional if using a real-time RTK solution)
- Septentrio RxTools (Optional if using an online PPP post-processing service)
How to determine the reference position of your base station?
Firstly, enable L5 with Septentrio Mosaic-X5.
- Connect the receiver to your PC via the USB port labeled as POWER+GPS.
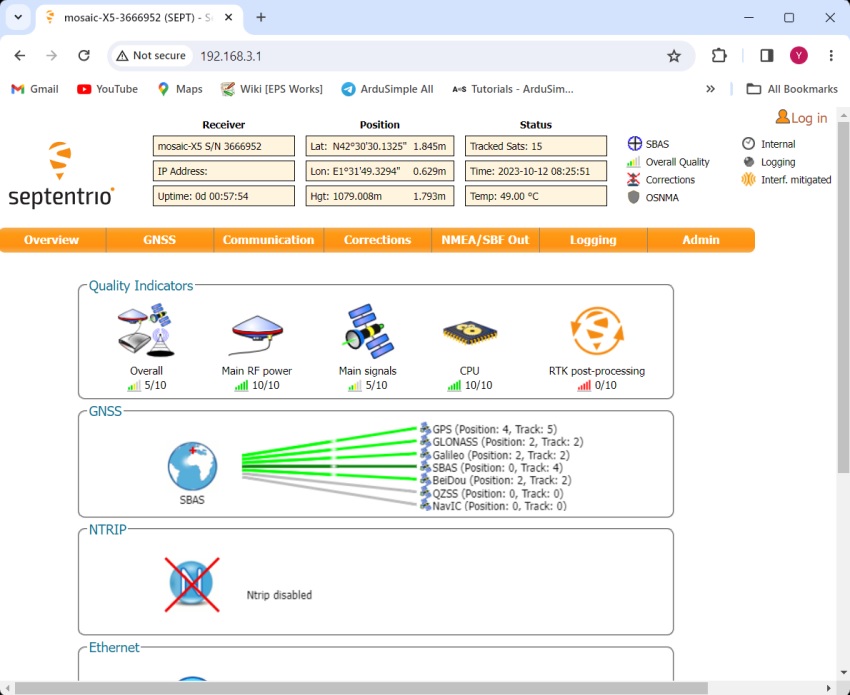
- Open Septentrio web interface by typing 192.168.3.1 in your browser.
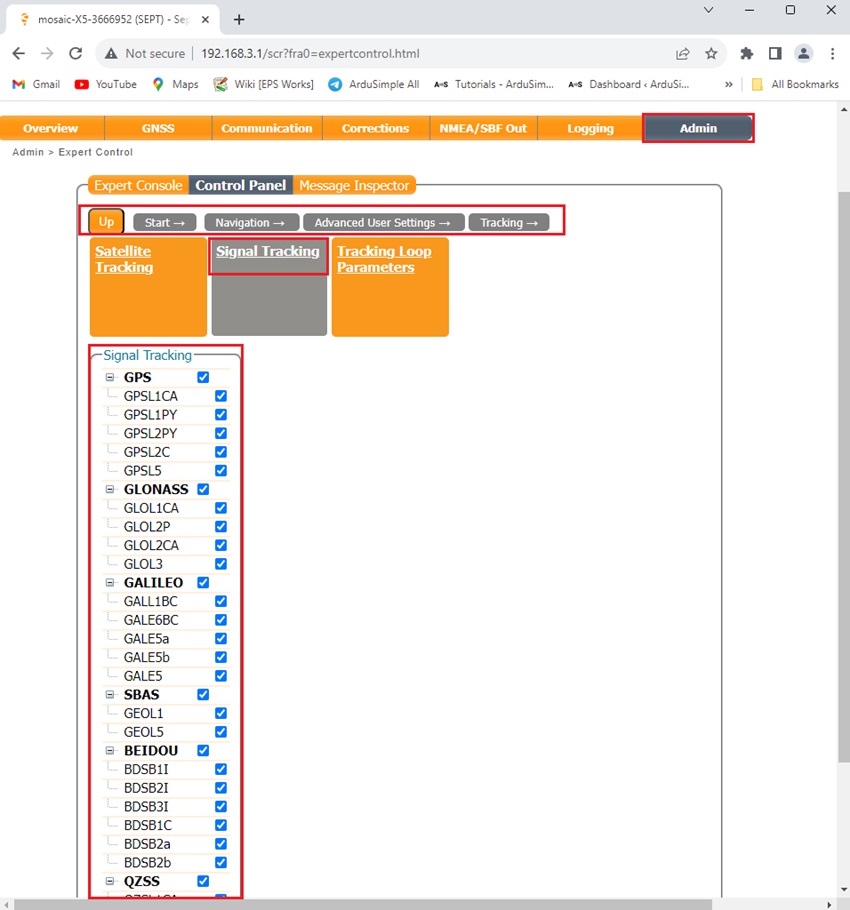
- L5 is disabled by default with Septentrio Mosaic-X5, thence we will enable L5 by going to Menu Bar–> Admin–>Expert Control–>Control Panel–>Navigation–>Advanced User Settings–>Tracking–>Signal Tracking.
Expand all satellite signals and select all band.
Click OK and save configuration.
Secondly, choose your preferred method to determine the geodetic reference position.
Using a known reference point
Using NTRIP service
Using an online PPP post-processing service
Using a known reference point
- Select an accurate and up-to date reference point, such as a geodetic control point or survey marker.
In this tutorial, we use the Senyals-geodesics of Catalunya.
Ensure that the reference point is situated in a location with a clear view of the sky, free from trees or other obstacles that may obstruct satellite signals. - Setting up the base station antenna above the reference point. With the use of a tribrach and tripod this can be done very accurately.

- The location of your base station will coincide with the Geodetic point’s location.
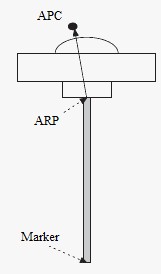
You can retrieve the geographic coordinates information from the geodetic point’s description.
Ensure to incorporate altitude information by adding the height difference between your Antenna Reference Point (ARP) and the marker.

Using NTRIP service
- Make sure there is a NTRIP service provider that covers your geographic location. If you are not aware of them, check this list. Most of these services are free but require registration.
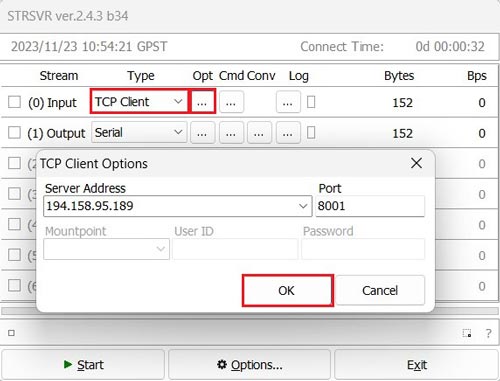
- Run STRSVR.
At Input section, connect to an RTK network to receive corrections.
Under Type choose the correction you use. Click the … icon under Opt to edit your correction service.
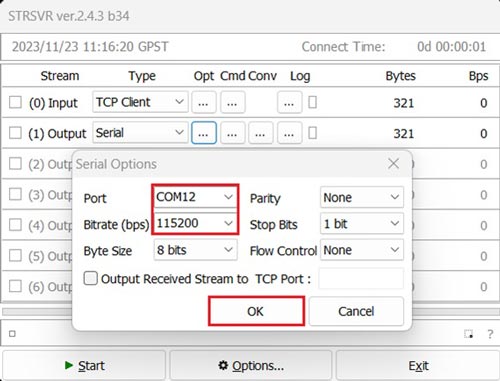
In this example, we are using the Andorra online correction service connected via TCP. - Select Serial at Output. Configure the appropriate COM port and Bitrate (Note: the COM Port number may differ from the image). Click OK.
- If you are using a NTRIP service, note that some NTRIP Caster will need the location of your base station.
Go to Options.
At Relay Messages choose (1)–>(0), which means sending Stream (1) Output to Stream (0) Input.
Thus the location information of your base station will be send back to NTRIP Caster.
Remember to enable NMEA GGA output of your receiver at the same COM port. If you don’t know how to do it, check the User Guide.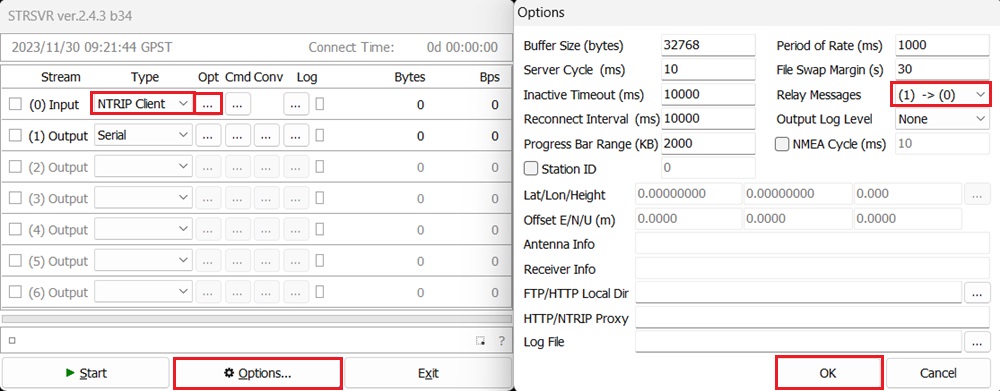
- Click Start and you will observe data transmission.
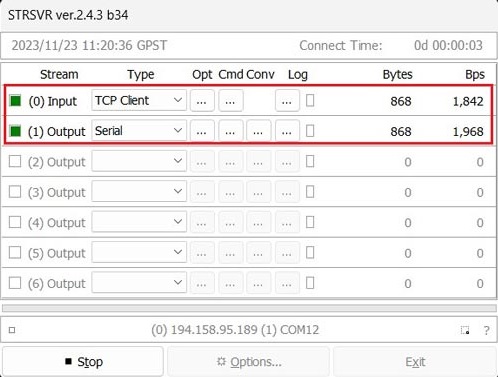
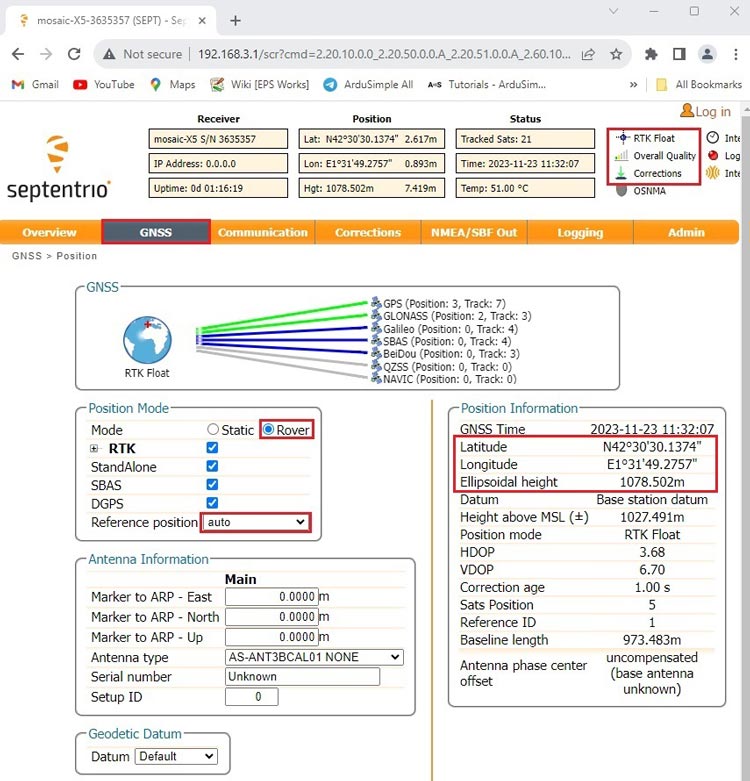
- Go back to Septentrio web interface. Go to GNSS–>Position. At position Mode select Rover. Reference position choose auto.
- In the upper-right corner, you should observe RTK Float or Fix with input corrections.
Record the fixed data as the location of your base station, which will be utilized in step 13. - For enhanced precision, consider logging data for a few hours. Perform post-processing using your preferred programming language, such as MATLAB or Python, to extract the coordinates of RTK fixed points from the log file and compute the mean value as your reference postion.
Using an online PPP post-processing service
- Log data from your receiver.
Use Septentrio RxTools to transform your SBF (Septentrio Binary Format) log file into RINEX. We will use the RINEX Observation file (.??O) in step 8.
If you don’t know how to do it, refer on tutorial How to generate RINEX files with simpleRTK3B.
If you have multiple files, save them in a single .zip or .tar archive. - CSRS-PPP has no requirement for the length of log data, but a more extended observation period enhances the accuracy of your base station’s location.
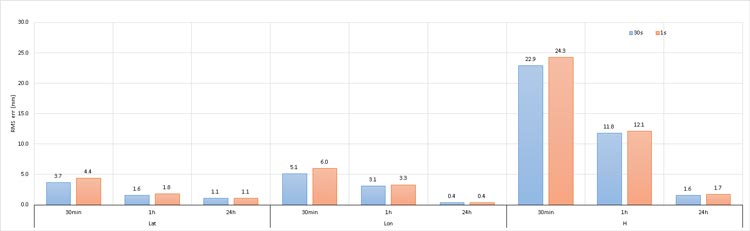
Note that in static mode, processing data at rates higher than 30 seconds does not improve the accuracy of the solution.
This is because CSRS-PPP uses precise GNSS clock products at a 30-second rate.
It is recommended to record a minimum of 1 hour, preferably 24 hours, of data with a 30-second interval .
The image below illustrates the Root Mean Square (RMS) values of variances among various observation session durations (30 minutes, 1 hour, and 24 hours), processed in static mode at 30-second and 1-second observation intervals. - CSRS-PPP service is free but requires registration. You can easily register on their website by providing your email and some basic information.
- After logging into your account, you can access the Processing mode.
Check Static.
If you are in North America, select NAD83 and choose the Epoch according to your location. Otherwise choose ITRF.
Click Choose file to upload your RINEX file.
Finally click Submit to PPP.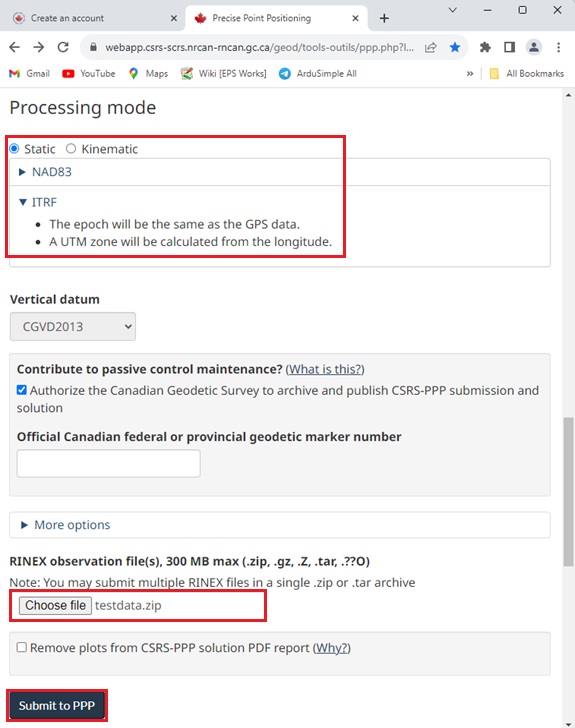
- After successfully submitting the data, you will see a note on the screen.
- You will receive an ultral-rapid result after about 1 hour.
Rapid result will be available about 12 hours after the end of each day.
The more accurate final result will take about 12-18 days, including GPS satellite orbits from the IGS, NRCan final GLONASS orbits, and an NRCan final clock combination.
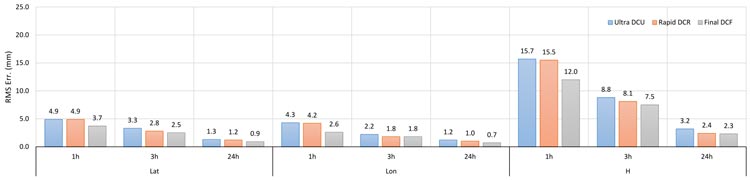
In the image below you can see the comparison of RMS errors between the CSRS-PPP ultra-rapid (DCU), rapid (DCR), and final (DCF) product lines
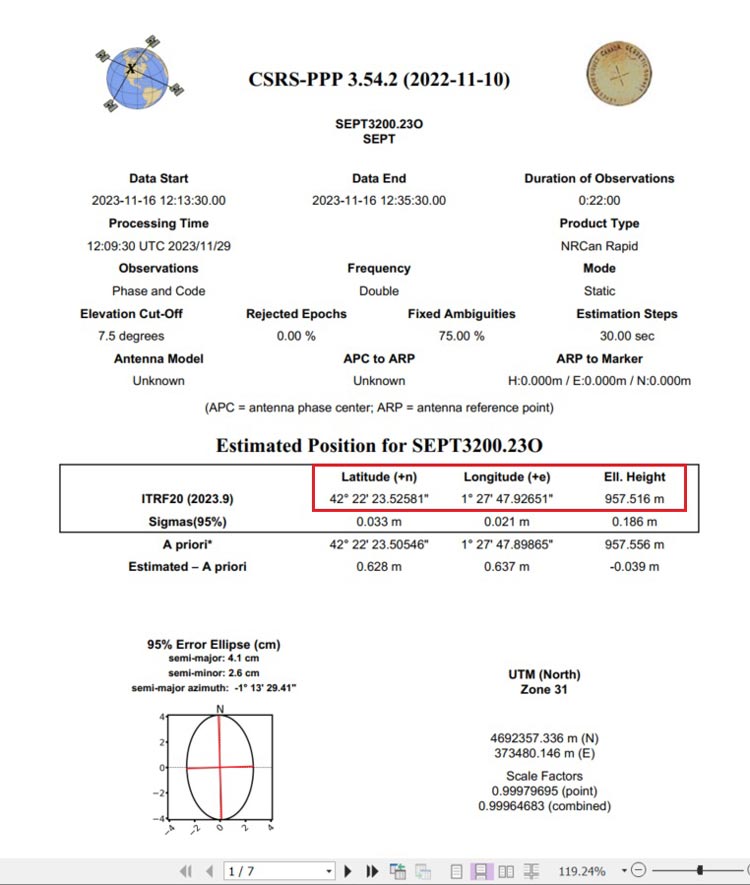
- In the PDF file of your result, you can find the estimated position for your base station.
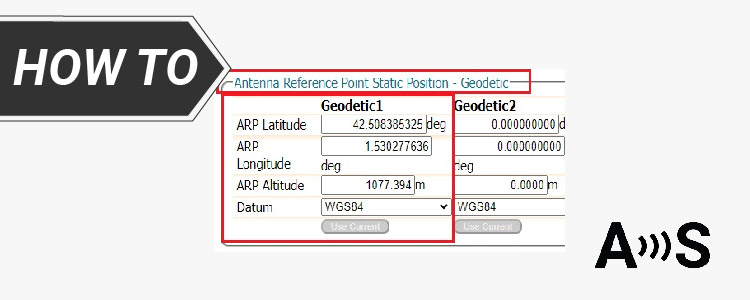
Thirdly, set the reference position as your antenna reference point static position.
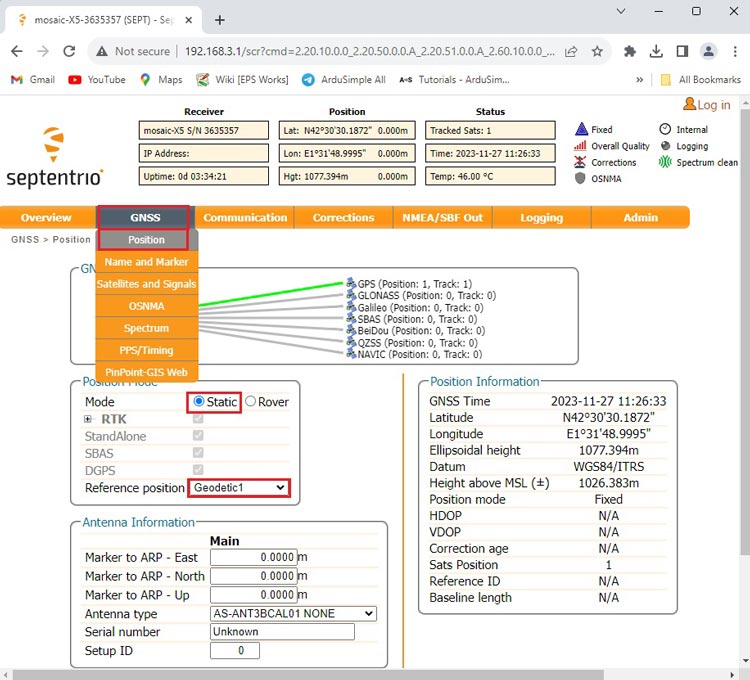
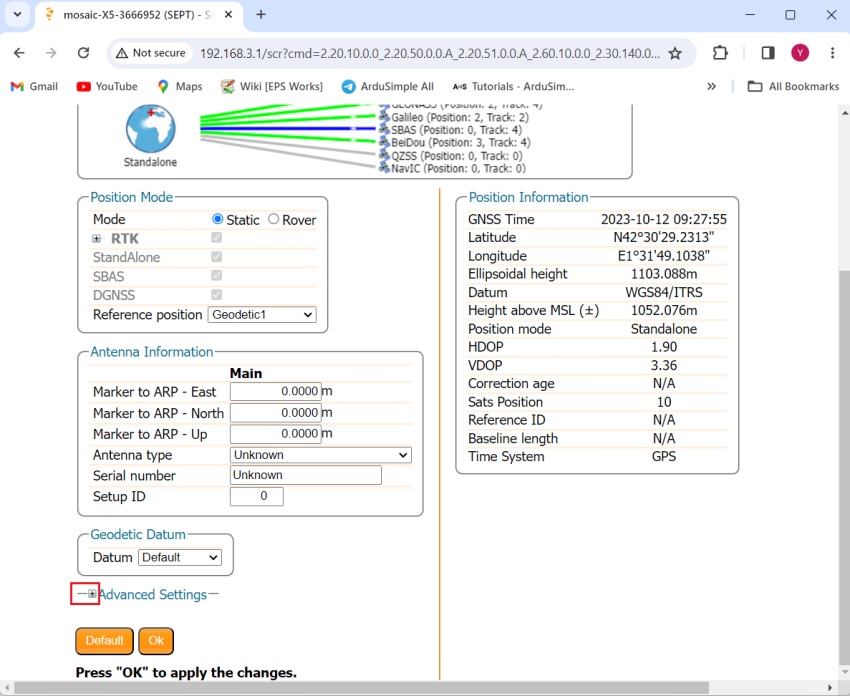
- Go back to Septentrio web interface. In the menu bar go to GNSS–>Position. At Mode choose Static. At Reference position select Geodetic 1
- Now scroll down and expand the Advanced Settings.
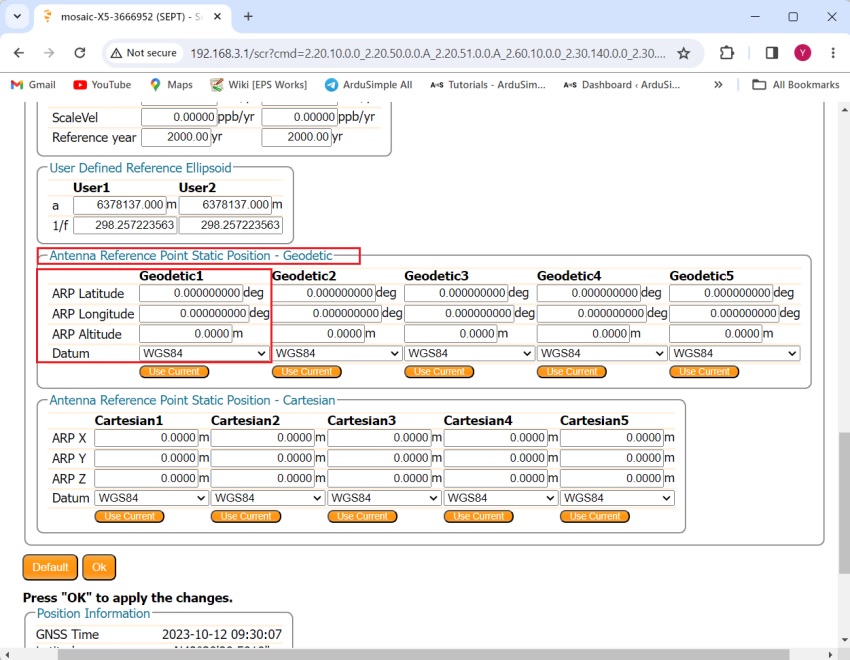
- Continue scrolling down until you find Antenna Reference Point Static Position – Geodetic.
Set the latitude, longitude and altitude you obtained from previous steps.
Note that the altitude to be set should be the ellipsoid altitude (if you need more info about different types of altitudes you can check out tutorial about GNSS altitudes).
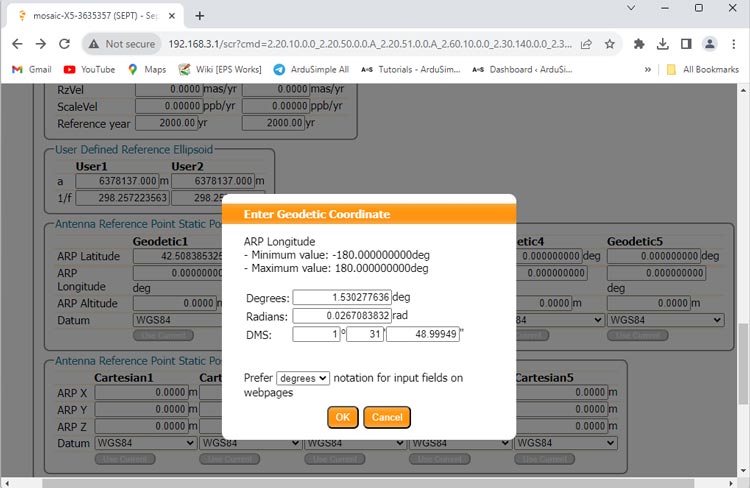
- You can set the coordinate with Degrees, Radians or DMS.
- Press Ok and Save the configuration.
Finally, enable correction data output.
- Select the interface you want to use to output correction data. If you are using one of the following plugins: Ethernet NTRIP Master, WiFi NTRIP Master, 4G NTRIP Master, you will configure RTCM3 output at COM2.
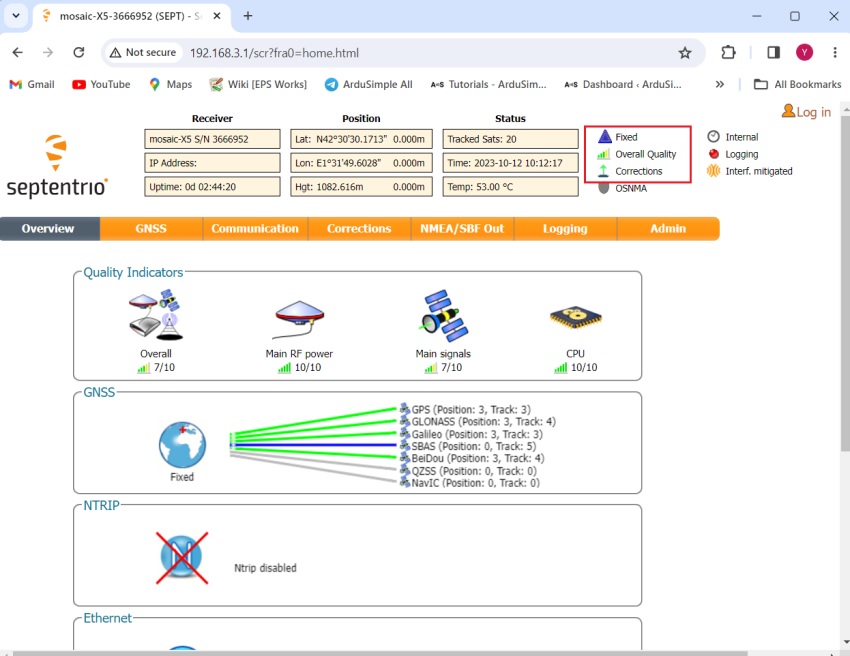
If you don’t know how to do it, refer to the tutorial How to configure simpleRTK3B as static base station. - Congratulations! Now you can use your receiver as a static base station with centimeter level absolute accuracy. On the up-right corner, you will see the position mode is Fixed and with correction output.
If you want to do this tutorial, we have all the products in stock and ready to be shipped:
 and
and